
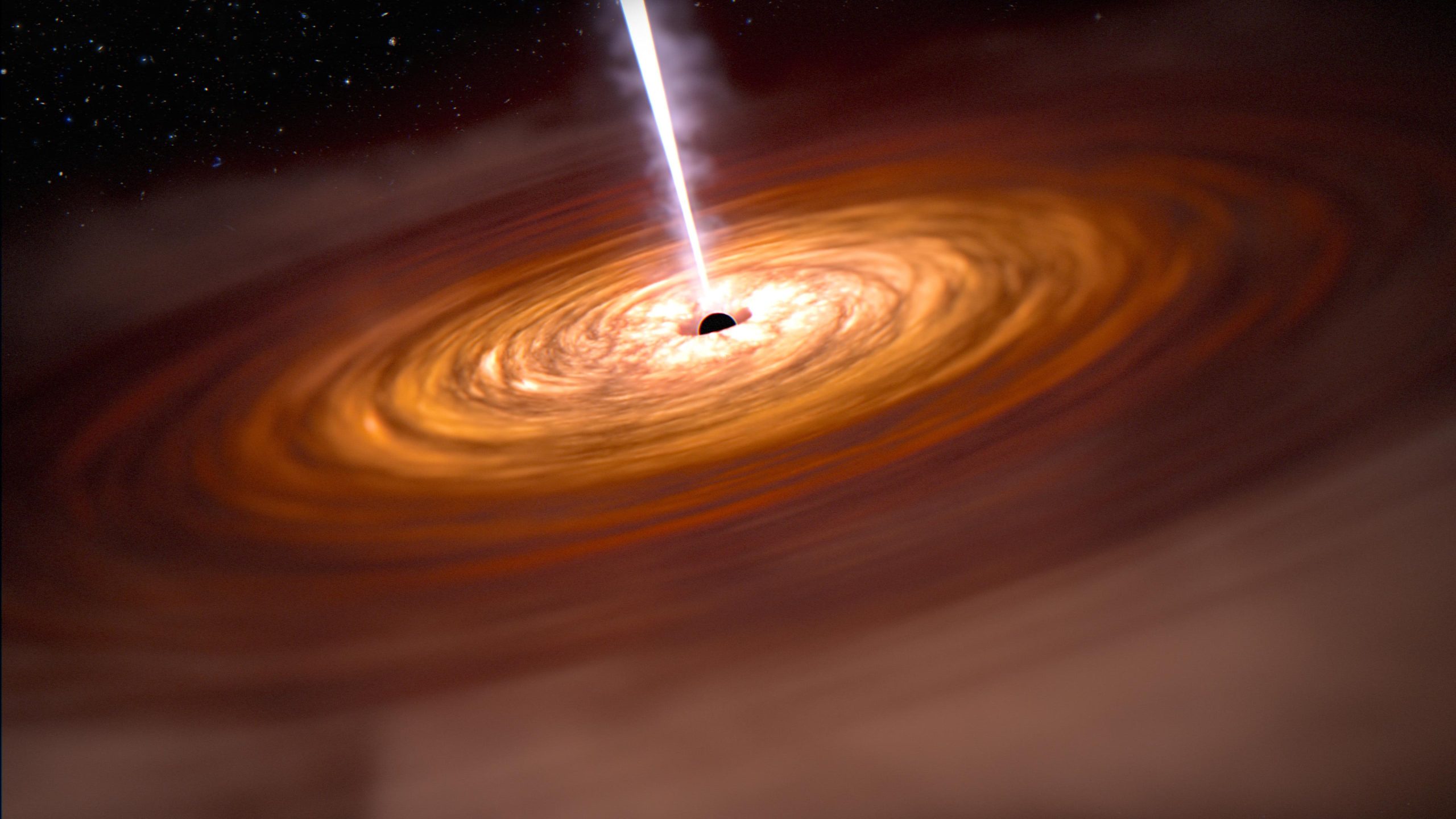
Illustration d’un quasar et d’une galaxie entourant le quasar. Selon des recherches menées par des scientifiques des universités de Sheffield et de Hertfordshire, les quasars, les objets les plus brillants et les plus puissants de l’univers, sont allumés par des galaxies en collision. Cette découverte fournit des informations importantes sur la compréhension du fonctionnement et de l’alimentation des quasars, contribuant à notre connaissance de l’histoire de l’univers et de l’avenir de la Voie lactée. Crédit : NASA, ESA, ASC, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Les scientifiques ont découvert l’un des plus grands mystères des quasars – les objets les plus brillants et les plus puissants de l’univers – en découvrant qu’ils sont allumés par des galaxies en collision.
- Découverts pour la première fois il y a 60 ans, les quasars peuvent briller aussi fort qu’un billion d’étoiles entassées dans un volume de la taille de notre système solaire, mais jusqu’à présent, on ne sait toujours pas ce qui pourrait déclencher une activité aussi vigoureuse.
- En observant 48 galaxies qui hébergent des quasars et en les comparant à plus de 100 galaxies non-quasars, les scientifiques ont découvert que le phénomène est alimenté par des collisions de galaxies.
- Lorsque deux galaxies entrent en collision, les forces gravitationnelles poussent d’énormes quantités de gaz vers les trous noirs supermassifs au centre du système de galaxies résiduelles résultant de la collision – juste avant que le gaz ne soit consommé par[{ » attribute= » »>black hole, it releases extraordinary amounts of energy in the form of radiation, resulting in a quasar
- The Milky Way is likely to experience its own quasar when it collides with the Andromeda galaxy in roughly five billion years’ time
First discovered 60 years ago, quasars can shine as brightly as a trillion stars packed into a volume the size of our Solar System. In the decades since they were first observed, it has remained a mystery what could trigger such powerful activity. New work led by scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Hertfordshire has now revealed that it is a consequence of galaxies crashing together.
The collisions were discovered when researchers, using deep imaging observations from the Isaac Newton Telescope in La Palma, observed the presence of distorted structures in the outer regions of the galaxies that are home to quasars.
Most galaxies have supermassive black holes at their centers. They also contain substantial amounts of gas – but most of the time this gas is orbiting at large distances from the galaxy centers, out of reach of the black holes. Collisions between galaxies drive the gas towards the black hole at the galaxy center; just before the gas is consumed by the black hole, it releases extraordinary amounts of energy in the form of radiation, resulting in the characteristic quasar brilliance.
The ignition of a quasar can have dramatic consequences for entire galaxies – it can drive the rest of the gas out of the galaxy, which prevents it from forming new stars for billions of years into the future.
This is the first time that a sample of quasars of this size has been imaged with this level of sensitivity. By comparing observations of 48 quasars and their host galaxies with images of over 100 non-quasar galaxies, researchers concluded that galaxies hosting quasars are approximately three times as likely to be interacting or colliding with other galaxies.
The study has provided a significant step forward in our understanding of how these powerful objects are triggered and fueled.
Professor Clive Tadhunter, from the University of Sheffield’s Department of Physics and Astronomy, said: “Quasars are one of the most extreme phenomena in the Universe, and what we see is likely to represent the future of our own Milky Way galaxy when it collides with the Andromeda galaxy in about five billion years.
“It’s exciting to observe these events and finally understand why they occur – but thankfully Earth won’t be anywhere near one of these apocalyptic episodes for quite some time.”
Quasars are important to astrophysicists because, due to their brightness, they stand out at large distances and therefore act as beacons to the earliest epochs in the history of the Universe. Dr. Jonny Pierce, Post-Doctoral Research Fellow at the University of Hertfordshire, explains:
“It’s an area that scientists around the world are keen to learn more about – one of the main scientific motivations for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was to study the earliest galaxies in the Universe, and Webb is capable of detecting light from even the most distant quasars, emitted nearly 13 billion years ago. Quasars play a key role in our understanding of the history of the Universe, and possibly also the future of the Milky Way.”
Reference: “Galaxy interactions are the dominant trigger for local type 2 quasars” by J C S Pierce, C Tadhunter, C Ramos Almeida, P Bessiere, J V Heaton, S L Ellison, G Speranza, Y Gordon, C O’Dea, L Grimmett and L Makrygianni, 13 February 2023, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad455






More Stories
Quelle est la prochaine grande nouveauté en matière de perte de poids ?
Une nouvelle découverte pourrait réécrire les livres sur la génétique
Compenser le sommeil le week-end pourrait réduire d’un cinquième le risque de maladie cardiaque – étude | Maladie cardiaque